Common Dental Issues in Cats and Dogs and Prevention
When it comes to pet care, we often focus on vaccinations, nutrition, and exercise. But what about their teeth? Dental health is frequently overlooked, despite being a major factor in a pet’s overall wellbeing. Pet dental problems are among the most common medical conditions seen by vets, affecting the majority of adult cats and dogs.
Without routine care and early intervention, these issues can lead to chronic pain, systemic illness, and tooth loss. Fortunately, most dental conditions are preventable with the right knowledge and care.
In this guide, we’ll uncover the most common dental issues in cats and dogs, explore their causes, and share practical steps for prevention—including targeted tips for cat gum disease prevention and avoiding dog tooth decay.
Why Dental Health Is Vital for Pets
Your pet’s mouth does far more than help them eat. It’s an essential gateway to their overall health. When oral hygiene is neglected, bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream, potentially damaging internal organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys.
Maintaining good oral health not only ensures a pain-free mouth but also reduces long-term health risks and veterinary bills. Prevention truly is the best medicine.
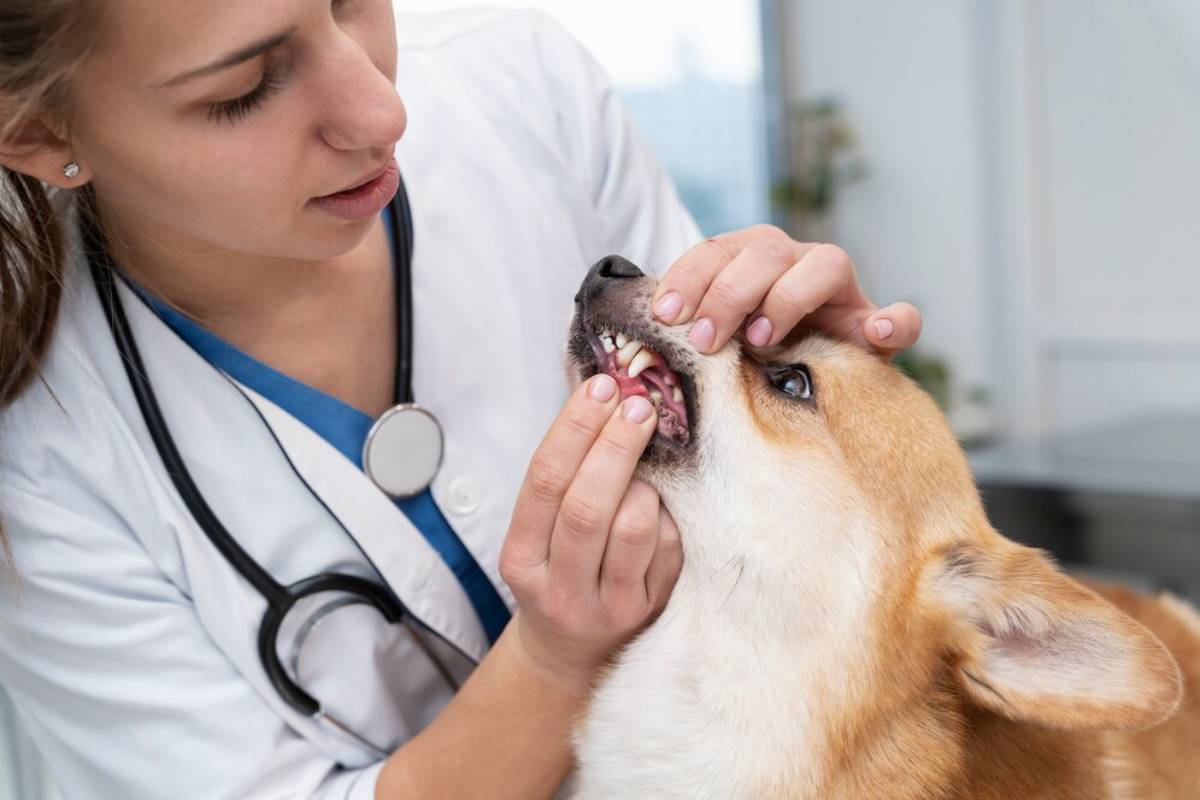
Common Dental Issues in Dogs
1. Periodontal Disease
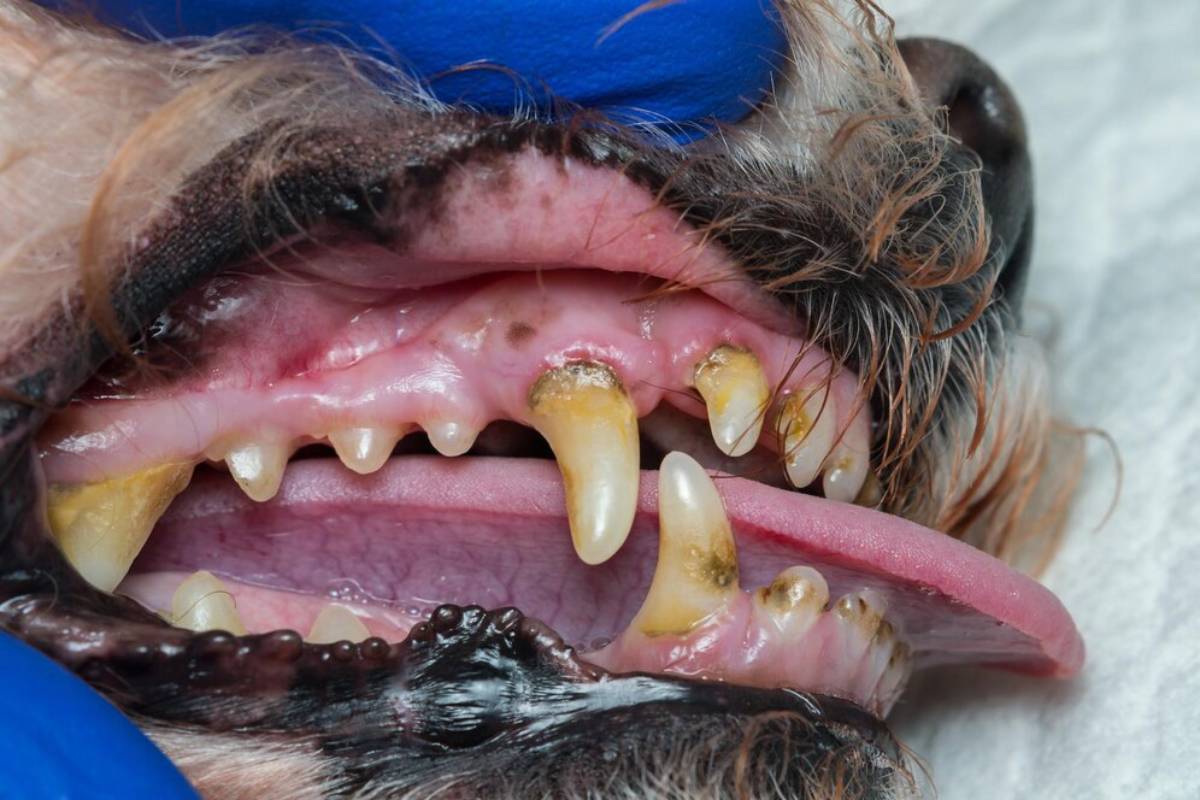
The most widespread dog dental problem, periodontal disease begins with plaque and progresses to tartar, gingivitis, and finally periodontitis—where gums recede and teeth loosen.
Signs to watch for:
- Bad breath
- Swollen or bleeding gums
- Yellow or brown tartar on teeth
- Difficulty chewing or loss of appetite
2. Tooth Decay (Cavities)
Though less common in dogs than humans, dog tooth decay can occur, particularly in molars. It’s often caused by sugary treats or leftover food particles.
Symptoms include:
- Dark spots on teeth
- Sensitivity when chewing
- Excessive drooling
- Visible holes in the tooth enamel
3. Fractured Teeth
Dogs that chew on hard toys, antlers, or bones can fracture their teeth—especially the large premolars used for crunching.
Look for:
- Sudden change in eating habits
- Swelling around the mouth
- Pawing at the mouth
Common Dental Issues in Cats
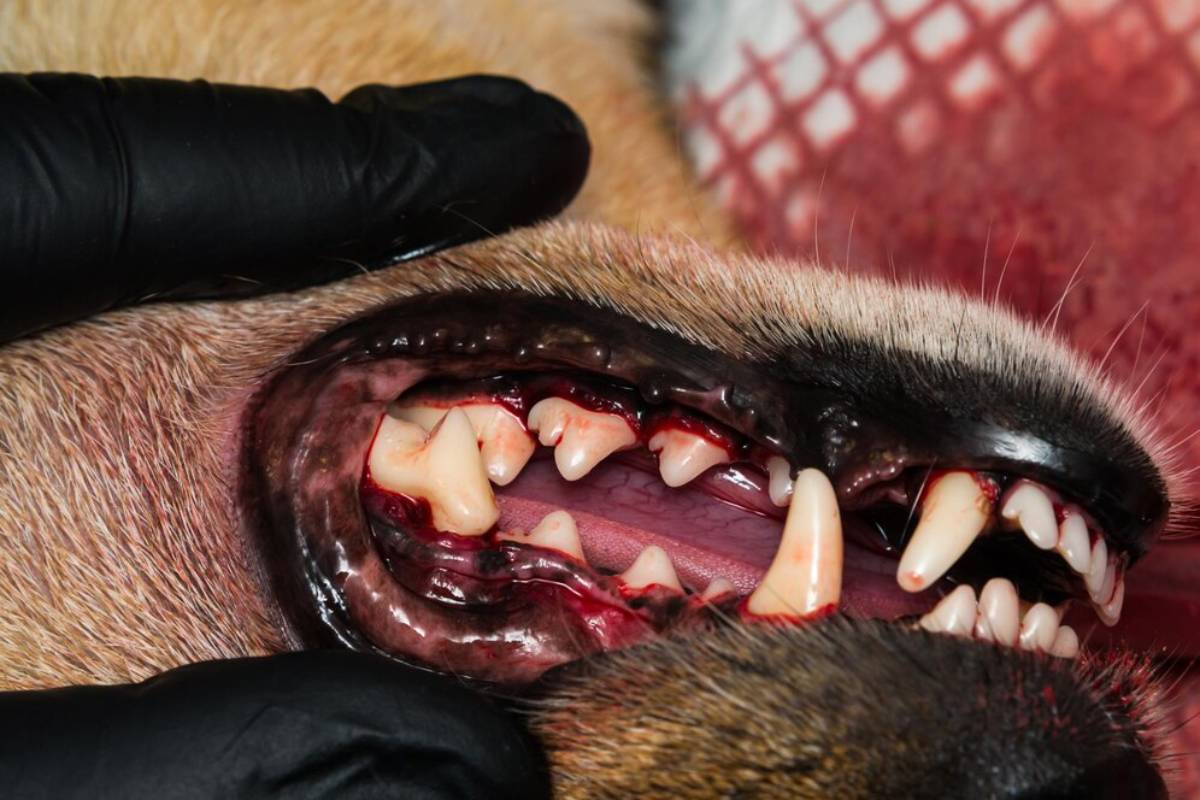
1. Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Inflamed, painful gums are common in cats and can lead to tooth loss if untreated. Cat gum disease prevention should be a priority, especially in middle-aged and older cats.
Warning signs:
- Red, inflamed gumlines
- Bleeding while eating
- Avoiding hard food
- Bad breath
2. Tooth Resorption
A unique and often painful condition in cats where the tooth structure breaks down from the inside out. It affects more than 50% of adult cats.
Symptoms include:
- Difficulty chewing
- Excessive salivation
- Oral bleeding
- Visible defects in the teeth
3. Stomatitis
This severe inflammatory condition causes ulcers and swelling in the mouth and throat, often linked to immune dysfunction or viral infections.
Watch for:
- Reluctance to eat
- Screaming or hiding when touched near the mouth
- Drooling and foul breath
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes pet dental problems helps in taking proactive steps. Common contributors include:
- Poor diet (especially soft, sticky foods)
- Lack of tooth brushing or dental care
- Genetic predispositions (e.g., small dog breeds and Persians)
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Autoimmune or viral diseases (especially in cats)
Prevention Tips: Protecting Your Pet’s Smile
1. Establish a Brushing Routine
Brushing your pet’s teeth is the most effective way to prevent plaque buildup and gum disease.
- Use pet-safe toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush
- Start slowly and positively
- Aim for brushing 3–5 times per week
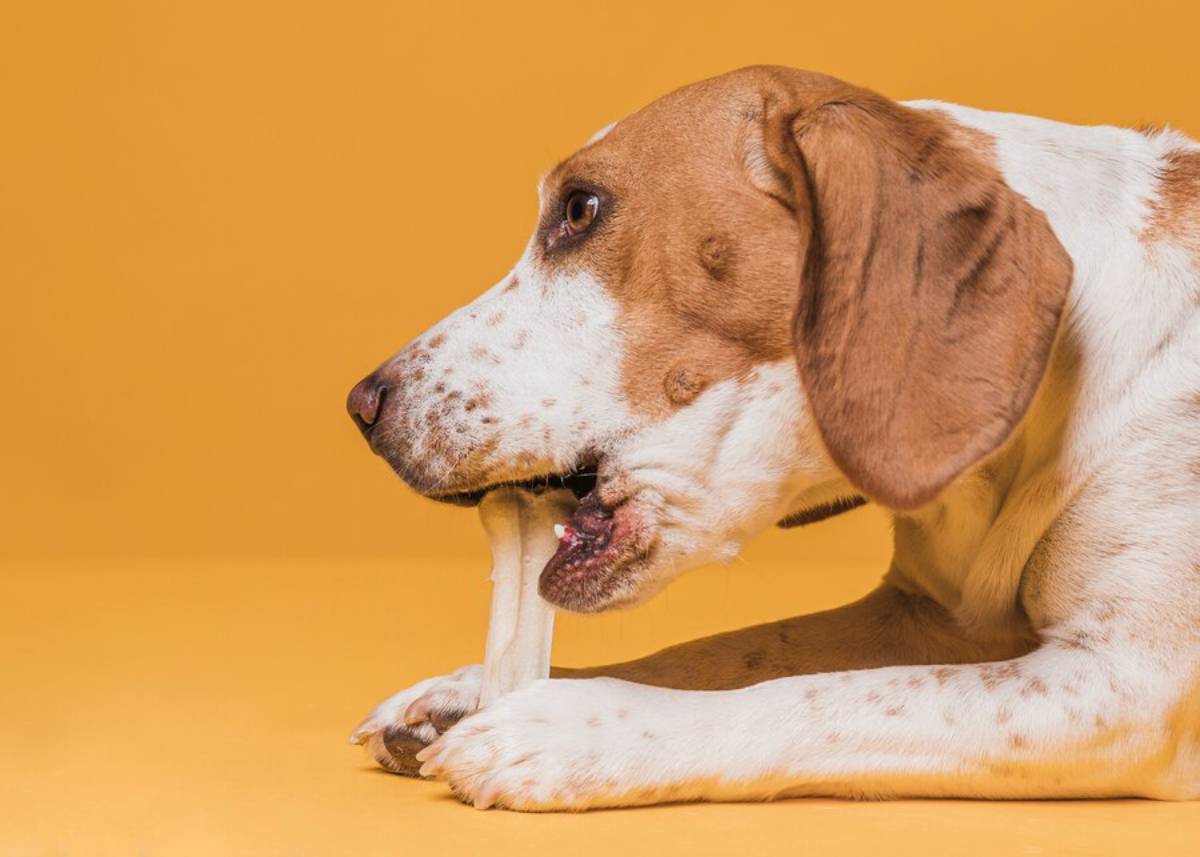

2. Offer Dental Chews and Toys
Chews can mechanically clean the teeth and massage the gums. Choose products approved by the Veterinary Oral Health Council (VOHC).
Avoid:
- Bones, antlers, and hard chews that can fracture teeth
3. Incorporate a Dental-Friendly Diet
Dry kibble with a specific dental formula can help reduce tartar build-up. Some prescription diets are designed to scrub teeth as your pet chews.
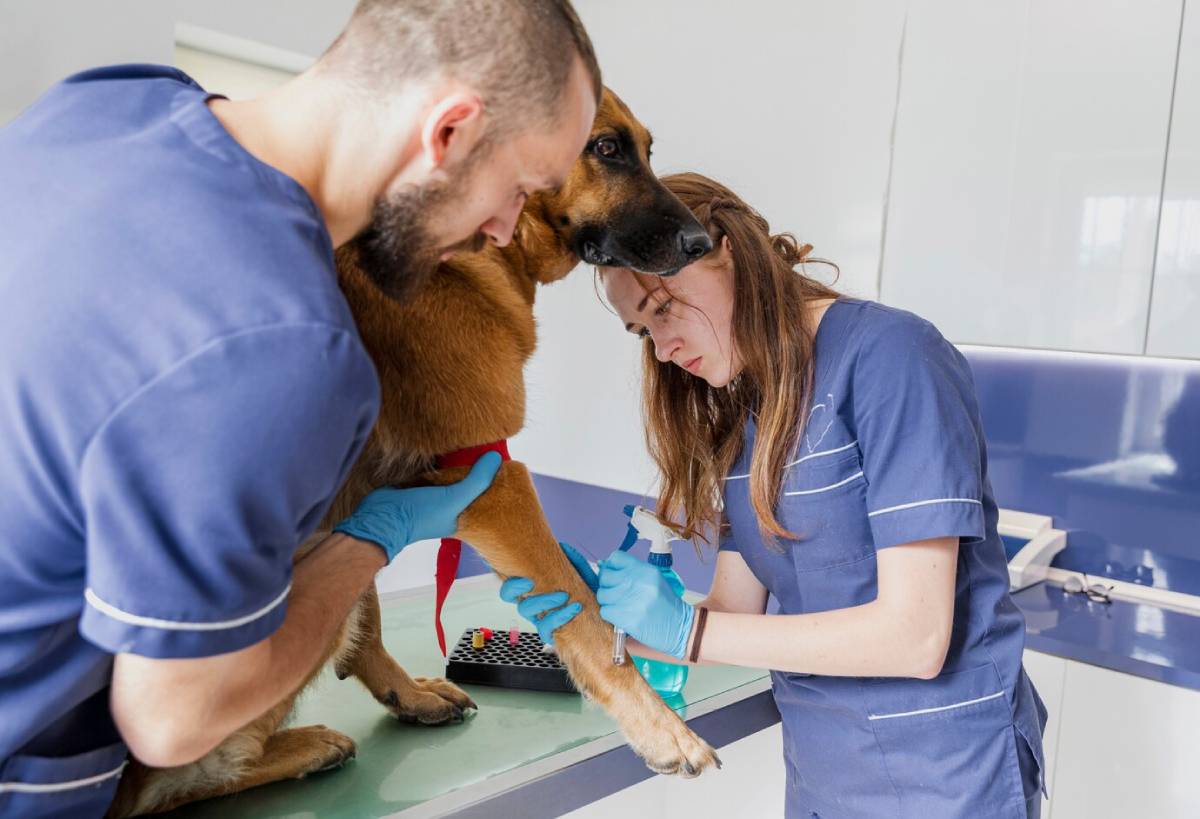
4. Schedule Regular Dental Check-Ups
Annual (or bi-annual for seniors) dental exams allow early detection of problems before they become severe.
- Your vet may recommend a professional clean under anaesthesia
- Dental X-rays may be needed for internal issues
5. Use Dental Water Additives or Gels
These are helpful additions between brushings:
- Reduce bacterial growth
- Freshen breath
- Promote healthier gums
Breed-Specific Dental Considerations
Small Dog Breeds
Breeds like Yorkies, Dachshunds, and Chihuahuas often suffer from overcrowded teeth and are at higher risk of periodontal disease. Start dental routines early and consider more frequent vet checks.
Brachycephalic Breeds
Flat-faced cats and dogs (e.g., Bulldogs, Persians) have misaligned jaws that can trap food and lead to faster tartar build-up. Use angled brushes and soft chews designed for these breeds.
Senior Pets
Older pets are more vulnerable to gum recession, root exposure, and infections. Transition to softer food if teeth are loose or missing, and visit your vet every 6–9 months for oral checks.
Healthy Mouth, Healthy Pet
Pet dental problems are common—but they don’t have to be inevitable. By brushing regularly, offering the right chews and food, and scheduling routine check-ups, you can safeguard your cat or dog from discomfort and disease.
Whether it’s cat gum disease prevention or guarding against dog tooth decay, proactive dental care improves the quality of life and supports long-term health.
Take action today: check your pet’s mouth, choose a dental-friendly treat, or book that overdue vet visit. A healthy smile isn’t just cosmetic—it’s a sign of a thriving, happy companion.


